#Opto-isolator module
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--optoelectronics--isolation-components-optocouplers/fod817dsd-onsemi-3492428
Thermal Heat sink, optocoupler relay module, Opto-isolator module
DIP4 Surface Mount Single Channel 70 V 5000 Vrms Phototransistor Optocoupler
#Optoelectronics#Isolation Components#Optocouplers#FOD817DSD#onsemi#Thermal Heat sink#relay module#Opto-isolator module#Phototransistor#optoelectronics#Thermal management#switch#Optical sensors#optocoupler relay
0 notes
Text
Optocoupler relay, isolated circuit, Optocoupler circuit, High voltage optocoupler
DIP6 SMT 1 Channel 400 V 4170 Vrms Zero-Cross Triac Optoisolator
#Optoelectronics#Isolation Components#Optocouplers#MOC3043SR2M#Onsemi#opto-isolator module#Triac opto isolator#Phototransistor Optocoupler#High speed#switch#Optocoupler relay module#isolated circuit#circuit#High voltage
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--optoelectronics--isolation-components-optocouplers/moc3043sr2m-onsemi-4354221
What is an opt isolator, Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology , Ethernet LANs,
DIP6 SMT 1 Channel 400 V 4170 Vrms Zero-Cross Triac Optoisolator
#Onsemi#MOC3043SR2M#Optoelectronics#Isolation Components#Optocouplers#opto-isolator#electronic component#optical coupler#opto isolator module#Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology#Ethernet LANs#transistor#circuit#photocoupler#optocoupler
1 note
·
View note
Text
This 16 Channel Relay Module consists of sixteen 5V relays and each one of the individual relay needs 15-20mA driver current. This module has a light coupling protection (optocoupler) which provide opto-isolation for safety purposes. This is a Relay module of 16 channel interface board that can be control various appliances, and other electronic equipment with large current. It can be controlled by Micro-controllers like Arduino, Raspberry-pi, ARM, TTL logic directly.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Future of Quantum Dot Lasers
For the past several decades, nanocrystals have been a staple of semiconductor laser technology. But, despite these impressive accomplishments, there remains much work to be done. One such challenge has been to develop spontaneous and coherent quantum dot lasers that function with electric excitation. This is a major milestone for the field of QD lasing and is a significant motivation to researchers and opto-electronic engineers working on various QD devices.
QD lasers have a number of advantages over conventional quantum well (QW) lasers and have recently shown the potential to address some major challenges facing today���s optical communication systems. These advantages are largely due to the unique properties of quantum dots, which allow them to be engineered for specific wavelengths of interest. In particular, the narrowbandwidth gain and high current densities associated with quantum dot active layers make it possible to achieve single-mode ridge-waveguide Fabry-Perot lasers. These structures are ideal for applications requiring high coherence and precision control of the light beam, such as optical data transmission and optical fiber sensing.

Additionally, the tunable bandgap of quantum dot materials provides the opportunity to create inexpensive and reliable infrared photodetectors that can be used for a wide variety of applications. Professor Arakawa techogle.co and his research group are actively pursuing the development of quantum dot infrared detectors, which could lead to practical remote sensing systems that can be mounted on satellites or other platforms.
The combination of these features makes quantum dot lasers the ideal building blocks for a new generation of photonic devices. These new devices are needed to support a wide range of applications including advanced optical communications, lab-on-a-chip platforms and wearable device technologies.
Compared to traditional silicon-based devices, photonics are more efficient and more capable, but there is still a bottleneck that prevents many of these benefits from being realized. This bottleneck comes in the form of the lasers, which must be made to operate seamlessly with silicon-based electronics.
A breakthrough in this area of technology is being made by scientists at Los Alamos National Laboratory, who are using a simple technique to create quantum dot lasers that are epitaxially integrated with silicon amplifiers, photodetectors and modulators. These devices have demonstrated clear advantages over standard silicon-based devices, such as record-low linewidth enhancement factors and high-repetition-rate mode locking.
Moreover, the low temperature dependence and threshold current density of QD-based material allows for longer device lifetimes by removing the need to utilize thermoelectric coolers. Similarly, the low sensitivity to optical feedback removes the need for an optical isolator, further decreasing technology website package costs. These results mark a significant step toward the realization of efficient, scalable III-V lasers on Si that are compatible with complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology. Ultimately, these new devices will enable faster, more reliable communications and other important applications. These innovations will open doors that were unimaginable just a few years ago. It will be possible to transmit massive amounts of information in a fraction of the time, and will bring powerful new capabilities to life that can transform our daily lives.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Elevating Reliability:Exploring GE MiCOM Agile P542's Advanced Protection

In the ever-evolving landscape of electrical infrastructure, ensuring the reliability and safety of power grids is paramount. Power utilities, substation operators, and engineers are continually seeking innovative solutions to protect and enhance the performance of electrical networks.. The GE MiCOM P542 relay has emerged as a high-speed current differential unit protection designed to tackle these challenges head-on. With a multitude of advanced features, this cutting-edge relay is set to revolutionize grid protection in overhead line and cable applications
Key Features of the GE MiCOM P542 Relay
1.)Differential Protection Adaptability:
The GE MiCOM P542 relay offers a high degree of flexibility when it comes to adapting to different substation topologies. Whether it's a two or three-terminal line/cable system or an in-zone transformer, this relay provides the required protection. It can also perform three-pole tripping, allowing for effective and comprehensive protection.
2.)Ideal for Distribution Applications:
The GE MiCOM P542 relay is not only a robust protection solution but also an economical choice for distribution applications. Its reliable performance and adaptable design make it a preferred option for power distribution networks.
3.)Small Case Width for Retrofitting:
Retrofitting existing systems is often a complex task, but the GE MiCOM P542 relay simplifies the process with its small case width. This feature facilitates easy integration into legacy systems, saving time and effort.
4.)Communication Protocols:
The relay supports various communication protocols, including IEC 60870-5-103, Modbus, and Courier. This flexibility ensures seamless integration with a wide range of monitoring and control systems, enhancing the overall functionality of the power network.
5.)Time Synchronization Options:
Time synchronization is crucial for maintaining a coordinated power system. The GE MiCOM P542 relay offers multiple time synchronization options, including RS485, IRIG-B (modulated/unmodulated), and Opto inputs. This ensures accurate timekeeping and synchronization across the network.
6.)Harsh Environment Coating:
To withstand challenging environmental conditions, the GE MiCOM P542 relay comes equipped with a standard harsh environment coating. This protective measure shields the relay against corrosive gases like H2S or SO2, ensuring its longevity and reliability in various settings.
7.)Multiple Setting Groups:
The GE MiCOM P542 relay offers four independent setting groups, allowing for versatile configuration options. This feature enables users to tailor the relay's settings to specific operational requirements, ensuring optimum performance and protection.
8.)Optimum Selectivity and Instantaneous Tripping
One of the standout features of the GE MiCOM P542 relay is its ability to ensure optimum selectivity. This is achieved by measuring the currents entering and leaving the protected plant item, which guarantees accurate fault detection and protection. The relay is programmed to provide instantaneous tripping in the event of an internal fault, ensuring the swift isolation of the faulted circuit.
Furthermore, the GE MiCOM P542 relay's stability extends to out-of-zone fault scenarios. It employs a proven characteristic that compares differential current with through current, making testing and fault analysis straightforward. The phase differential elements incorporated in this relay consistently detect solid and resistive faults, enabling precise faulted phase selection, tripping, and indication.
Conclusion
The GE MiCOM P542 relay is a vital component in modern power systems, providing high-speed current differential unit protection for overhead lines and cables. Its adaptability to different substation topologies, communication protocol support, time synchronization options, and robust construction make it an ideal choice for distribution applications. With its small case width and the ability to withstand harsh environments, the GE MiCOM P542 relay simplifies retrofitting tasks and ensures reliable protection. This relay's optimum selectivity, instantaneous tripping, and consistent fault detection capabilities are key factors in safeguarding power infrastructure and maintaining a stable and efficient electrical grid.
Digital & Smart Grid Enterprises is a trusted supplier of authentic and cost-effective GE MiCOM Agile P542 Transmission Protection Relay
Our equipment can improve the efficiency of power systems, while our customized services cater to leading sectors and panel builders.
Contact us at +917021624024 or email [email protected] click here if you would like to know more about
0 notes
Text
Uses for an optical isolator

Opto isolators are also used in computer systems for data transfer by modulating the output voltage of a primary circuit and using light as a medium. Opto isolators are ideal for the recording industry because they reduce all interference that would have been generated by passing a voltage directly from one circuit component to another. Photodiodes and phototransistors are the two most common light receivers. They also have a small light source or LED to send signals and a photosensitive component to receive transmissions. Both types of optoisolators have a casing to prevent outside light from interfering with the device operation. Analog optoisolators reproduce the input signal and provide an analog output that is used when the signal amount is the circuit requirements’ overriding factor. The digital type changes its output to match the signal received and is used when pulse or bit output is required between circuits. There are two types of optoisolators-digital and analog. This allows the input of the secondary component to be equal or slightly less than the output of the primary component. The electricity is then directed to the other components within that circuit. The light beam travels down the closed channel until it reaches the photosensor that then converts the light back into electricity. A voltage from a circuit is used as the isolator’s power source and is used to produce a beam of near-infrared light. Opto isolators consist of a power source, a near-infrared LED, a closed channel, and a photosensor. They now cost less than US$1 and continue to get cheaper. They are good for quality control in the recording industry, and can be used in other industrial applications such as electroencephalography, data transfer, and optoelectronics. The cost of these devices have significantly reduced since they were first invented. Opto isolators regulate voltage levels by converting electricity into a beam of light. This prevents voltage spikes from impacting more than a single circuit and decreases the overall interference and noise that occurs with traditional communications connections. In order to achieve protection, SLAVE device must be powered by other power source than MASTER device (TapHome Core and Modules).An opto isolator is an electronic device that prevents high voltages from components in one side of a circuit from damaging or interfering with components on the other side of the same circuit. The isolator must always be installed on the side of one of the protected devices (MASTER) - as close as possible to it. MASTER side is protected device, typically TapHome Core control unit In this case, also power source must be galvanically isolated - the easiest way is to use separate power source. This is the most common situation when when connecting TapHome modules in the garden house, or meteo station on the roof. TapHome module or other RS485 device device is connected to TapHome BUS, and the wire or device itself is outside of the lightning protection.External device is powered by other (typically its internal) power source and does not have galvanic or optical isolation.Use of optical isolator is obligatory if one of the conditions is met: Optical isolator protects TapHome control unit when connecting Modbus RTU or other RS485 bus device to it. Optical isolator supports bi-directional "half-duplex" transmission for RS485 networks.

0 notes
Text
Hacking an old Nintendo Zapper into a wireless remote
Those of us who have experienced the Nintendo Zapper while playing games such as Duck Hunt will probably have fond memories of it. However, with the rapid disappearance of CRT TVs and the aging of the physical mechanisms, YouTuber DuctTape Mechanic wanted to give an old Zapper a new lease on life. His modification integrated a small RF transmitting module into the top of the device, allowing it to be switched on by the trigger’s microswitch. With everything in place inside the Zapper, he moved onto the receiver.
In order to get the incoming signals from the RF transmitter and turn them into an action, a receiver circuit was necessary. First, he soldered an RF module to a breadboard, along with an opto-coupling IC that isolates the sensitive electronics. From here, the receiver connects to an Arduino Uno that sets a pin high or low to turn the relay module + opto-coupler circuit on or off. In its current configuration, the Zapper acts like a toggle switch, where one press toggles everything to on while a subsequent press toggles everything off.
As seen in the video below, being able to ‘zap’ your lights with the Nintendo Zapper looks really cool, and it will be interesting to see where DuctTape Mechanic takes it from here.
youtube
The post Hacking an old Nintendo Zapper into a wireless remote appeared first on Arduino Blog.
Hacking an old Nintendo Zapper into a wireless remote was originally published on PlanetArduino
0 notes
Text
This 16 Channel Relay Module consists of sixteen 12V relays and each one of the individual relays needs 15-20mA driver current. This module has coupling protection (optocoupler) which provides opto-isolation for safety purposes. This is a Relay module of 16 channel interface board that can be control various appliances, and other electronic equipment with a large current. It can be controlled by Micro-controllers like Arduino, Raspberry-pi, ARM, TTL logic directly.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

16 Channel Relay 5V Module
This 16 Channel Relay Module consists of sixteen 5V relays and each one of the individual relay needs 15-20mA driver current. This module has a light coupling protection (optocoupler) which provide opto-isolation for safety purposes. This is a Relay module of 16 channel interface board that can be control various appliances, and other electronic equipment with large current. It can be controlled by Micro-controllers like Arduino, Raspberry-pi, ARM, TTL logic directly. The power supply it has is LM2596 Power Supply that can control various appliances and other electronic equipment with a large current.
Features:
5V relay with AC contact capacity of 10A 250V and optocoupler protection.
Onboard power supply module, doesn't need any external power supply.
The module can be used as microcontroller development board module and also as appliance control, PLC extended output.
It is using the industry’s top -quality isolation optocouplers, strong anti-jamming ability, stable performance.
The 1-16 road can be any full on/off or any road.
All interfaces can be directly connected through the terminal leads, very convenient.
Indication LED’s for Relay output status.
Buy this 16 Channel Relay: https://quartzcomponents.com/products/16-channel-relay-5v-module
0 notes
Photo

PM100CSE120 Powerex #ic #igb #igbt #module Https://www.slw-ele.com; Email: [email protected]





#PM100CSE120 Powerex PM100CSE120 New Powerex / Mitsubishi MadePM100CSE120 IGBT Mitsubishi 100A 1200V, PM100CSE120 pictures, PM100CSE120 price, #PM100CSE120 supplier ------------------------------------------------------------------- Email: [email protected]
https://www.slw-ele.com/pm100cse120.html
-------------------------------------------------------------------
FEATURE
a) Adopting new 4th generation planar IGBT chip, which performance is improved by 1µm fine rule process.
b) Using new Diode which is designed to get soft reverse
recovery characteristics.
•3φ 100A, 1200V Current-sense IGBT for 15kHz switching
• Monolithic gate drive & protection logic
• Detection, protection & status indication circuits for overcurrent, short-circuit, over-temperature & under-voltage
• Acoustic noise-less 18.5/22kW class inverter application
PRECAUTIONS FOR TESTING
1. Before appling any control supply voltage (VD), the input terminals should be pulled up by resistores, etc. to their corresponding supply voltage and each input signal should be kept off state.
After this, the specified ON and OFF level setting for each input signal should be done.
2. When performing “OC” and “SC” tests, the turn-off surge voltage spike at the corresponding protection operation should not
be allowed to rise above VCES rating of the device.
(These test should not be done by using a curve tracer or its equivalent.)
NOTES FOR STABLE AND SAFE OPERATION ;
•Design the PCB pattern to minimize wiring length between opto-coupler and IPM’s input terminal, and also to minimize the
stray capacity between the input and output wirings of opto-coupler.
•Quick opto-couplers : TPLH, TPLH ≤ 0.8µs. Use High CMR type. The line between opto-coupler and intelligent module
should be shortened as much as possible to minimize the floating capacitance.
•Slow switching opto-coupler : recommend to use at CTR = 100 ~ 200%, Input current = 8 ~ 10mA, to work in active.
•Use 4 isolated control power supplies (VD). Also, care should be taken to minimize the instantaneous voltage charge of the
power supply.
•Make inductance of DC bus line as small as possible, and minimize surge voltage using snubber capacitor between P and N
terminal.
•Use line noise filter capacitor (ex. 4.7nF) between each input AC line and ground to reject common-mode noise from AC line
and improve noise immunity of the system.
Powerex / Mitsubishi MadePM100CSE120 IGBT Mitsubishi 100A 1200V
0 notes
Text
Acousto-Optic Modulators Market: Trend, Outlook, Application - Forecast till 2025
The Acousto-Optic Modulators Market distinguished players alongside the corporate profiles and coming up with adopting by them. This helps the client of the Acousto-Optic Modulators report back to gain a transparent read of the competitive landscape, and consequently arrange Acousto-Optic Modulators market methods. Associate in Nursing isolated section with prime key players is provided within the report that provides whole analysis of value, gross, revenue.
The global Acousto-Optic Modulators market report study provides intelligence studies guaranteeing relevant and fact-based analysis that facilitates purchasers to perceive the importance and impact of market dynamics. This analysis report covers this standing and future prospect for the world Acousto-Optic Modulators market. The report offers the elaborate Acousto-Optic Modulators market summary, development, and phase by sort, application, and region. Additionally, Acousto-Optic Modulators marketing research report introduces the market competition summary among the most important firms and companies’ profiles.
Get Exclusive Sample of Report on Acousto-Optic Modulators market is available @ https://www.acquiremarketresearch.com/sample-request/389522
A thorough competition analysis that covers perceptive information on business leaders is meant to assist potential market entrants and existing players in competition with the correct direction to make their selections. Market structure analysis discusses intimately Acousto-Optic Modulators firms with their profiles, revenue shares in the market, comprehensive portfolio of their offerings, networking and distribution methods, regional market footprints, and far a lot of.
Get Discount of Report on Acousto-Optic Modulators market is available @ https://www.acquiremarketresearch.com/discount-request/389522
Major Market Players Covered In This Report:
Gooch&Housego, Brimrose, Isomet Corporation, AA Opto-Electronic Company, APE GmbH, IntraAction Corp, Lightcomm Technology Co.,Ltd
According to the report, the product expense of the Acousto-Optic Modulators market is segmented into:
Fiber-Coupled Acousto-optic Modulators,Free-Space Acousto-optic Modulators
Apart from that, the application market is segmented into:
Material processing, Medical (surgery, beauty), Laser Printing, Laser imaging and displays, Research
Acousto-Optic Modulators Market
Regions & Countries Mentioned within the Acousto-Optic Modulators Report:
North America (United States)
Europe (Germany, France, UK)
Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, India)
Latin America (Brazil)
The Middle East & Africa
Frequently asked questions about Acousto-Optic Modulators marketing research Report:
What are the most recent trends, and methods followed by leading companies?
What is the market share of every Major Player laid out in this report?
What are the opportunities for fruitful internal secretion investors and market aspirants?
What are the most important product varieties, and that applications are known?
What is the market size, and demand for fruitful internal secretion on a world level?
What is the CAGR price of a fruitful internal secretion Market?
Direct Buy Acousto-Optic Modulators Report market @ https://www.acquiremarketresearch.com/buy-now/389522
The origination of Acousto-Optic Modulators report has been backed by providing purchasers with a holistic read of market conditions and future possibilities/opportunities to reap most profits out of their businesses and assist in deciding. Our team of in-house analysts and consultants works indefatigably to know your desires and recommend the simplest doable solutions to satisfy your analysis necessities.
Our team at Acousto-Optic Modulators report follows a rigorous method of information validation, that permits North American country to publish reports from publishers with minimum or no deviations. The Acousto-Optic Modulators report collects, segregates, and publishes over five hundred reports annually that cater to products and services across varied domains.
About Us
Acquire Market Research is a market research-based company empowering companies with data-driven insights. We provide Market Research Reports with accurate and well-informed data, Real-Time with Real Application. A good research methodology proves to be powerful and simplified information that applied right from day-to-day lives to complex decisions helps us navigate through with vision, purpose, and well-armed strategies. At Acquire Market Research, we constantly strive for innovation in the techniques and the quality of analysis that goes into our reports. We are aware of the cascading impact of the information on a global level from overall businesses to people and the cutting edge solutions for achieving positive and impactful decisions.
Contact Us
https://www.acquiremarketresearch.com/
#Acousto-Optic Modulators#Acousto-Optic Modulators 2021#Acousto-Optic Modulators Type#Acousto-Optic Modulators Outlook#Acousto-Optic Modulators Market
0 notes
Link
Extension Cable Optional 650mm long cable for Base Unit to Expansion Unit interconnection, which enables a two tier configuration.,The following Analogue and Temperature Modules (Combined Analogue Input & Output Module, Analogue Input Module, Analogue Output Module, Thermocouple Input Module, PT100 Input Module) have opto-isolation between analogue and digital circuitry, they also employ dc to dc converters to isolate the supply from the base unit or power supply. However, there is no isolation between analogue channels. Additional Modules for Mitsubishi FX1S, FX1N & FX2N PLC's Products in this range are for use with FX1S, FX1N and FX2N PLC, unless specified otherwise. All are DIN rail mount and are 90mm high and 87mm deep. The width varies and is tabled below. All of the following products, except the Extension Cable, attach directly to the right hand end of the previous unit, block or module using the short integral lead.
0 notes
Text
400+ TOP POWER ELECTRONICS Interview Questions and Answers pdf
POWER ELECTRONICS Interview Questions with Answers :-
1. What is holding current in SCR? It is the minimum current required to hold the SCR in forward conduction state. When the forward current becomes less than holding current, SCR turns from forward conduction state to forward blocking state. 2. What is latching current in SCR? It is the minimum current required to latch(turn on) the SCR from forward blocking state to forward conduction state. 3. What are the different turn on methods of SCR? Forward voltage triggering Gate Triggering dv/dt triggering Temperature triggering Light triggering 4. What is snubber circuit? The snubber circuit is used for the dv/dt protection of the SCR. It is a series combination of a resistor and a capacitor in parallel with the SCR. 5. What is hard switching of the thyristor? When gate current is several times higher than the required gate current, the SCR is said to be hard fired. It reduces the turn ON time and enhances the di/dt capability.

POWER ELECTRONICS Questions 6. What is firing angle? The angle between the zero crossing of the input voltage and the instant the SCR is fired is called as delay angle or firing angle. 7. What is meant by SOA? SOA - Safe Operating Area determines the voltage and current boundary within which the Power Device can be operated without destructive failure. 8. What are the main components used for isolating the Power Circuits, Power Semiconductor from the low-power circuit? Opto-Couplers, Transformers 9. Name some of the current controlled (current driven) devices... SCR, GTO, GTR 10. Name some of the voltage driven ( Voltage controlled) devices IGBT, MCT, IGCT, SIT 11. What is duty cycle? It is the ratio of the ON time of the chopper to total time period of the chopper. D = Ton / 12. Can fuses with an AC voltage rating be used in a DC applications? Fuses must be rated for the voltage AC or DC in which they will be used. Generally, fuses have a DC voltage rating that is half of the maximum AC voltage rating. 13. What are the characteristics of ideal Opamp? Infinite open loop voltage gain Infinite input impedance Zero output impedance Infinite Bandwidth Zero offset voltage 14. For High voltage applications will you prefer MOSFET or IGBT? For High voltage applications we have to use IGBT. Because MOSFETs are low voltage devices. ie, Their voltage rating is lesser than IGBT. General rule is MOSFETs are suitable for applications which has breakdown voltage less than 250V. The IGBTs are suitable for applications which has breakdown voltage upto 1000V. 15. For High frequency applications will you prefer MOSFET or IGBT? Why? For High frequency applications, MOSFET is the right choice of the device. Because MOSFET has low switching losses compare to that of IGBT. General rule of thumb is for low-frequency applications having frequency range upto 20kHz, we have to use IGBT. For high frequency applications having frequency range of more than 200kHz, we have to use MOSFET. POWER ELECTRONICS Interview Questions :: 16. What are the advantages of free wheeling diode in rectifier circuit? The input power factor is improved. It prevents the output voltage from becoming negative. The Load current waveform is improved. 17. What are the types of commutation? Natural commutation Forced commutation 18. What is natural commutation? The process of the current flowing through the thyristor goes through a natural zero and enable the thyristor to turn off is called as natural commutation. 19. What is forced commutation? The process of the current flowing through the thyristor is forced to become zero by external circuitry is called as forced commutation. 20. What are the types of commutation with respect to commutation process? Voltage commutated chopper Current commutated chopper Load commutated chopper 21. What is meant by cyclo-converter? It is also known as frequency changer. It converts input power at one frequency to output power at another frequency with one stage conversion. 22. What are the types of cyclo-converters? Step up cyclo-converter Step down cyclo-converter. 23. What is step down cyclo-converter? It is the converter whose output frequency is less than the input frequency. 24. What is step up cyclo-converter ? It is the converter whose output frequency is more than the input frequency. 25. What does the Voltmeter in AC mode show? Is it RMS value or peak value? Multimeter in AC mode shows RMS value of the voltage or current. Also when it is DC mode it will show the RMS value only. 26. What is the necessity to use the special machines? General purpose motors (Induction motors, synchronous motors) are neither precision speed nor precision position motors. For many automated systems require high precise speed and high precise positioning motors. In such cases special purpose motors like stepper motors, PMDC motors etc. are used. 27. What are the control strategies of chopper? The control strategies of chopper are Pulse width modulation PWM (Variable TON, Constant frequency) Frequency modulation (Constant TON or TOFF, Variable frequency) Current Limit Control (CLC) 28. What is delay angle or what is firing angle of phase controlled rectifier? The delay angle is the angle at which thyristors are triggered after zero crossing. After zero crossing of supply voltage, one pair of thyristors is forward biased. ie, After delay angle(α) these SCRs are triggered. 29. What is Universal Motor? It is defined as a motor which can be operated either on DC or single-phase AC supply at approximately the same speed and output. The universal motor is built exactly like a series DC motor. But a series DC motor cannot be run as a universal motor, even though both motors look the same internally and externally. We cannot use these motors in the industrial applications due to the low efficiency (25% -35%). It has high starting torque and a variable speed characteristic. It runs at dangerously high-speed on no load. 31. Give some examples of power electronics applications in the day-to-day life? We can list a huge number of power electronics applications. Few of the applications which we can see in our daily life are UPS - Uninterruptible Power Supply SMPS - Switch Mode Power Supply Speed Control of Motors ICU 32. What is meant by PMDC? PMDC stands for Permanent Magnet DC Motor A Permanent Magnet DC Motor is similar to an ordinary dc shunt motor except that its field is provided by permanent magnets instead of salient-pole wound field structure. There are three types of permanent magnets used for such motors namely; (i) Alnico Magnets (ii) Ceramic magnets (iii) Rare-earth magnets The major advantages are low noise, small size, high-efficiency, low manufacturing cost. 33. What is meant by commutation? The process of changing the direction of current flow in a particular path of the circuit. It is used to turn off the SCR. 34. Two Bulbs Of 100w And 40w Respectively Connected In Series Across A 230v Supply Which Bulb Will Glow Bright And Why? Since two bulbs are in series they will get equal amount of electrical current but as the supply voltage is constant across the bulb(P=V^2/R).So the resistance of 40W bulb is greater and voltage across 40W is more (V=IR) so 40W bulb will glow brighter. 35. What Is Meant By Knee Point Voltage? Knee point voltage is calculated for electrical Current transformers and is very important factor to choose a CT. It is the voltage at which a CT gets saturated.(CT-current transformer). 36. What Is Reverse Power Relay? Reverse Power flow relay are used in generating station's protection. A generating stations is supposed to fed power to the grid and in case generating units are off,there is no generation in the plant then plant may take power from grid. To stop the flow of power from grid to generator we use reverse power relay. 37. What Are The Advantage Of Free Wheeling Diode In A Full Wave Rectifier? It reduces the harmonics and it also reduces sparking and arching across the mechanical switch so that it reduces the voltage spike seen in a inductive load. 38. What Is The Full Form Of Kvar? We know there are three types of power in Electrical as Active, apparent & reactive. So KVAR is stand for ``Kilo Volt Amps with Reactive component. 39. Definition Of Power Electronics? Power electronics refers to control and conversion of electrical power by power semiconductor devices wherein these devices operate as switches. 40. What Is The Main Purpose Of Power Electronics? The main task of power electronics is to control and convert electrical power from one form to another. AC to DC conversion: Rectifier is used for converting an AC voltage to a DC voltage. Rectifier applications: Variable speed dc drives, Battery chargers, DC power supplies and Power supply for a specific application like electroplating. DC to AC conversion: Inverter circuit is used to convert DC voltage to an alternating voltage. Inverter applications: Emergency lighting systems, AC variable speed drives, Un-interrupted power supplies and Frequency converters. DC to DC conversion: A dc-to-dc converter circuit was called a chopper. Chopper applications: DC drive, Battery charger and DC power supply. AC to AC conversion: A cycloconverter converts an AC voltage to another AC voltage. Cycloconverter applications: It is rarely used. Can be used for controlling the speed of an AC traction motor 41. What Are The Different Operation Regions Of The Thyristor (scr)? SCR or thyristor will have three regions of operations based on the mode in which the device is connected in the circuit. Reverse blocking region: When the cathode of the thyristor is made positive with respect to the anode and no gate signal is applied. In this region SCR exhibits the reverse blocking characteristics similar to diode. Forward blocking region: In this region the anode of the thyristor is made positive with respect to the cathode and no gate signal is applied to the thyristor. A small leakage current flow in this mode of operation of the thyristor. Forward conduction region: when the forward voltage applied between the anode and cathode increases at particular break over voltage avalanche breakdown takes place and thyristor starts conducting current in forward direction. By this type of triggering the device damages the scr. Hence a gate signal is applied before the forward break over voltage to trigger the scr. 42. What Are The Losses That Occur In A Thyristor During Working Conditions? Forward conduction losses Loss due to leakage current during forward and reverse blocking Switching losses at turn on turn off Gate triggering loss 43. What Are The Advantages Of Freewheeling Diode In Rectifier Circuit? The input power factor is improved. It prevents the output voltage from becoming negative. Load current waveform is also improved. 44. Explain The Function Of Cyclo-converter? It is also known as frequency changer. It converts input power at one frequency to output power at another frequency with one stage conversion. 45. What Is An Inverter? A device which converts dc power into ac power at desired output voltage and frequency is called as Inverter. 46. Define Circuit Turn Off Time It is defined as the time during which a reverse voltage is applied across the thyristor during its commutation process. 47. Why The Circuit Turn Off Time Should Be Greater Than Thyristor Turn Off Time? If the circuit turn off time is less than the thyristor turn off time the device may turn on at an undesired instant resulting in commutation failure. 48. What Is Chopper? A dc Chopper is equivalent to the transformer in ac circuit. It is a static switch used to get the variable dc voltage from a constant dc voltage. 49. What Are The Types Of Commutation? (or) Turn Off Methods? Natural commutation Forced commutation 50. What Is Natural Commutation? The process of the current flowing through the thyristor goes through a natural zero and enable the thyristor to turn off is called as natural commutation. 51. What Is Forced Commutation? The process of the current flowing through the thyristor is forced to become zero by external circuitry is called as forced commutation. 52. What Is Step Down Chopper? In step down chopper, the average output voltage is less than the input supply voltage. It is also known as Buck converter. 53. What Is Step Up Chopper? In step up chopper, the average output voltage is more than the input supply voltage. It is also known as Boost converter. 54. What Is Voltage Commutation? The process of a charged capacitor momentarily reverse biases the conducting SCR and turns it off is called as voltage commutation. 55. What Is Current Commutation? The process of a current pulse is made to flow in the reverse direction through the conducting SCR and thus made the net SCR current becomes zero, consequently turn off the SCR is called as current commutation. 56. What Are The Advantages Of Current Commuted Chopper? The advantages of current commutated chopper is; Commutation is reliable as load current is less than the peak commutation current The auxiliary SCR is naturally commutated as its current passes through zero value. The capacitor always remains charged with the correct polarity. 57. What Is Load Commutation? In load commutation, the load current flowing through the thyristor either becomes zero or is transferred to another device from the conducting SCR. 58. Name Some Of The Current Controlled (current Driven) Devices? SCR, GTO, GTR. 59. Name Some Of The Voltage Driven (voltage Controlled) Devices. IGBT, MCT, IGCT, SIT. 60. What Is Meant By Pulse Triggered Devices? To turn on these kind of devices single pulse of short duration is sufficient. Continuous gate voltage of entire on time is not required. It will avoid the hard triggering. Example: Thyristor, GTO 61. What Is Meant By Level-sensitive Devices? In order to maintain these kind of devices in on-state, we need to apply continuous gate current /voltage. Some of the level sensitive devices are: MOSFET, IGBT, MCT, IGCT 62. What Are The Advantages Of Igbt Over Bjt, Mosfet? IGBT has Lower turn on and turn off times than BJT Lower on state conduction losses than MOSFET Excellent safe operating area 63. Why Igbt Is Very Popular Nowadays? Lower hate requirements Lower switching losses Smaller snubber circuit requirements 64. What Are The Different Methods To Turn On The Thyristor? Forward voltage triggering Gate triggering dv/dt triggering Temperature triggering Light triggering 65. What Is The Difference Between Power Diode And Signal Diode? Power diode Constructed with n-layer, called drift region between p+ layer and n+ layer. The voltage, current and power ratings are higher. Power diodes operate at high speeds. Signal diode Drift region is not present. The voltage, current and power ratings are Lower Operates at higher switching speed. 66. Igbt Is A Voltage Controlled Device. Why? Because the controlling parameter is gate-emitter voltage. 67. Power Mosfet Is A Voltage Controlled Device. Why? Because the output (drain) current can be controlled by gate-source voltage. 68. Power Bjt Is A Current Controlled Device. Why? Because the output (collector) current can be controlled by base current. 69. What Is The Relation Between α & β? 70. What Are The Different Types Of Power Mosfet? N-channel MOSFET P-channel MOSFET 71. How Can A Thyristor Turned Off? A thyristor can be turned off by making the current flowing through it to zero. 72. Define Latching Current? The latching current is defined as the minimum value of anode current which it must attain during turn on process to maintain conduction when gate signal is removed. 73. Define Holding Current? The holding current is defined as the minimum value of anode current below which it must fall to for turning off the thyristor. 74. What Is A Snubber Circuit? It consists of a series combination of a resistor and a capacitor in parallel with the thyristors. It is mainly used for dv / dt protection. 75. What Losses Occur In A Thyristor During Working Conditions? Forward conduction losses Loss due to leakage current during forward and reverse blocking. Switching losses at turn-on and turn-off. Gate triggering loss. 76. Define Hard-driving Or Over-driving? When gate current is several times higher than the minimum gate current required, a thyristor is said to be hard-fired or over-driven. Hard-firing of a thyristor reduces its turn-on time and enhances its di/dt capability. 77. Define Circuit Turn Off Time? It is defined as the time during which a reverse voltage is applied across the thyristor during its commutation process. 78. Why Circuit Turn Off Time Should Be Greater Than The Thyristor Turn-off Time? Circuit turn off time should be greater than the thyristor turn-off time for reliable turn-off, otherwise the device may turn-on at an undesired instant, a process called commutation failure. 79. What Is The Turn-off Time For Converter Grade Scrs And Inverter Grade Scrs? Turn-off time for converter grade SCRs is 50 – 100 ms turn-off time for converter grade SCRs and inverter grade SCRs and for inverter grade SCRs is 3 – 50 ms. 80. What Are The Advantages Of Gto Over Scr? Elimination of commutation of commutating components in forced commutation, resulting in reduction in cost, weight and volume. Reduction in acoustic noise and electromagnetic noise due to elimination of commutation chokes. Faster turn-off, permitting high switching frequencies. Improved efficiency of the converters. 81. What Is Meant By Phase Controlled Rectifier? It converts fixed ac voltage into variable dc voltage. 82. Mention Some Of The Applications Of Controlled Rectifier? Steel rolling mills, printing press, textile mills and paper mills employing dc motor drives. DC traction Electro chemical and electro-metallurgical process Portable hand tool drives Magnet power supplies HVDC transmission system 83. What Is The Function Of Freewheeling Diodes In Controlled Rectifier? It serves two process. It prevents the output voltage from becoming negative. The load current is transferred from the main thyristors to the freewheeling diode, thereby allowing all of its thyristors to regain their blocking states. 84. What Are The Advantages Of Free Wheeling Diodes In A Controlled In A Controlled Rectifier? Input power factor is improved. Load current waveform is improved and thus the load performance is better. 85. What Is Meant By Delay Angle? The delay angle is defined as the angle between the zero crossing of the input voltage and the instant the thyristor is fired. 86. What Are The Advantages Of Single Phase Bridge Converter Over Single Phase Mid-point Converter? SCRs are subjected to a peak-inverse voltage of 2Vm in a fully controlled bridge rectifier. Hence for same voltage and current ratings of SCrs, power handled by mid-point configuration is about In mid-point converter, each secondary winding should be able to supply the load power. As such, the transformer rating in mid-point converter is double the load rating. 87. What Is Commutation Angle Or Overlap Angle? The commutation period when outgoing and incoming thyristors are conducting is known as overlap period. The angular period, when both devices share conduction is known as the commutation angle or overlap angle. 88. What Are The Different Methods Of Firing Circuits For Line Commutated Converter? UJT firing circuit. The cosine wave crossing pulse timing control. Digital firing schemes. 89. Give An Expression For Average Voltage Of Single Phase Semiconverters? Average output voltage Vdc = (Vm /Π) (1 + cosα). 90. What Is Meant By Input Power Factor In Controlled Rectifier? The input power factor is defined as the ratio of the total mean input power to the total RMS input volt-amperes. PF = ( V1 I1 cos φ1 ) / ( Vrms Irms) where V1 = phase voltage, I1 = fundamental component of the supply current, φ1 = input displacement angle, Irms = supply rms current. 91. What Are The Advantages Of Six Pulse Converter? Commutation is made simple. Distortion on the ac side is reduced due to the reduction in lower order harmonics. Inductance reduced in series is considerably reduced. 92. What Is Meant By Natural Commutation? Here the current flowing through the thyristor goes through a natural zero and enable the thyristor to turn off. 93. What Is Meant By Forced Commutation? the thyristor is forced to become zero by external circuitry. 94. What Is Meant By Dc Chopper? A dc chopper is a high speed static switch used to obtain variable dc voltage from a constant dc voltage. 95. What Are The Applications Of Dc Chopper? Battery operated vehicles Traction motor control in electric traction Trolley cars Marine hoists Mine haulers Electric braking. 96. What Is Meant By Step-up And Step-down Chopper? In a step- down chopper or Buck converter, the average output voltage is less than the input voltage. In a step- up chopper or Boost converter, the average output voltage is more than the input voltage. 97. Write Down The Expression For Average Output Voltage For Step Down Chopper? Average output voltage for step down chopper V0 = α Vs, α is the duty cycle. 98. Write Down The Expression For Average Output Voltage For Step Up Chopper? Average output voltage for step down chopper Vs V0 = ------ 1 - α α is the duty cycle. 99. What Is Meant By Duty-cycle? Duty cycle is defined as the ratio of the on time of the chopper to the total time period of the chopper. It is denoted by α. 100. What Are The Two Types Of Control Strategies? Time Ratio Control (TRC) Current Limit Control method (CLC) 101. What Is Meant By Trc? In TRC, the value of Ton / T is varied in order to change the average output voltage. 102. What Are The Two Types Of Trc? Constant frequency control Variable frequency control 103. What Is Meant By Fm Control In A Dc Chopper? In frequency modulation control, the chopping frequency f (or the chopping period T) is varied. Here two controls are possible. On-time Ton is kept constant Off period Toff is kept constant. 104. What Is Meant By Pwm Control In Dc Chopper? In this control method, the on time Ton is varied but chopping frequency is kept constant. The width of the pulse is varied and hence this type of control is known as Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). 105. Write Down The Expression For The Average Output Voltage For Step Down And Step Up Chopper? Average output voltage for step down chopper is VO = α VS. Average output voltage for step up chopper is VO = α VS x . 106. What Are The Different Types Of Chopper With Respect To Commutation Process? Voltage commutated chopper. Current commutated chopper. Load commutated chopper. 107. What Is Meant By Voltage Commutation? In this process, a charged capacitor momentarily reverse biases the conducting thyristor and turn it off. 108. What Is Meant By Current Commutation? In this process, a current pulse is made to flow in the reverse direction through the conducting thyristor and when the net thyristor current becomes zero, it is turned off. 109. What Is Meant By Load Commutation? In this process, the load current flowing through the thyristor either becomes zero or is transferred to another device from the conducting thyristor. 110. What Are The Advantages Of Current Commutated Chopper? The capacitor always remains charged with the correct polarity. Commutation is reliable as load current is less than the peak commutation current ICP. The auxiliary thyristor TA is naturally commutated as its current passes through zero value. 111. What Are The Advantages Of Load Commutated Chopper? Commutating inductor is not required. It is capable of commutating any amount of load current. It can work at high frequencies in the order of kHz. Filtering requirements are minimal. 112. What Are The Disadvantages Of Load Commutated Chopper? For high power applications, efficiency becomes very low because of high switching losses at high operating frequencies. Freewheeling diode is subjected to twice the supply voltage. Peak load voltage is equal to twice the supply voltage. The commutating capacitor has to carry full load current at a frequency of half chopping frequency. One thyristor pair should be turned-on only when the other pair is commutated. This can be realized by sensing the capacitor current that is alternating. 113. What Is Meant By Inverter? A device that converts dc power into ac power at desired output voltage and frequency is called an inverter. 114. What Are The Applications Of An Inverter? Adjustable speed drives Induction heating Stand-by aircraft power supplies UPS HVDC transmission 115. What Are The Main Classification Of Inverter? Voltage Source Inverter Current Source Inverter 116. Why Thyristors Are Not Preferred For Inverters? Thyristors require extra commutation circuits for turn off which results in increased complexity of the circuit. For these reasons thyristors are not preferred for inverters. 117. How Output Frequency Is Varied In Case Of A Thyristor? The output frequency is varied by varying the turn off time of the thyristors in the inverter circuit, i.e. the delay angle of the thyristors is varied. 118. Give Two Advantages Of Csi? CSI does not require any feedback diodes. Commutation circuit is simple as it involves only thyristors. 119. What Is The Main Drawback Of A Single Phase Half Bridge Inverter? It require a 3-wire dc supply. 120. Why Diodes Should Be Connected In Antiparallel With Thethyristors In Inverter Circuits? For RL loads, load current will not be in phase with load voltage and the diodes connected in anti parallel will allow the current to flow when the main thyristors are turned off. These diodes are called feedback diodes. 121. What Types Of Inverters Require Feedback Diodes? VSI with RL load. 122. What Is Meant A Series Inverter? An inverter in which the commutating elements are connected in series with the load is called a series inverter. 123. What Is The Condition To Be Satisfied In The Selection Of L And C In A Series Inverter? 4L R2 C 124. What Is Meant A Parallel Inverter? An inverter in which the commutating elements are connected in parallel with the load is called a parallel inverter. 125. What Are The Applications Of A Series Inverter? The thyristorised series inverter produces an approximately sinusoidal waveform at a high output frequency, ranging from 200 Hz to 100kHz. It is commonly used for fixed output applications such as Ultrasonic generator. Induction heating. Sonar Transmitter Fluorescent lighting. 126. How Is The Inverter Circuit Classified Based On Commutation Circuitry? Line commutated inverters. Load commutated inverters. Self commutated inverters. Forced commutated inverters. 127. What Is Meant By Mcmurray Inverter? It is an impulse commutated inverter which relies on LC circuit and an auxiliary thyristor for commutation in the load circuit. 128. What Are The Applications Of A Csi? Induction heating Lagging VAR compensation Speed control of ac motors Synchronous motor starting. 129. What Is Meant By Pwm Control? In this method, a fixed dc input voltage is given to the inverter and a controlled ac output voltage is obtained by adjusting the on and off periods of the inverter components. This is the most popular method of controlling the output voltage and this method is termed as PWM control. 130. What Are The Advantages Of Pwm Control? The output voltage can be obtained without any additional components. Lower order harmonics can be eliminated or minimized along with its output voltage control. As the higher order harmonics can be filtered easily, the filtering requirements are minimized. 131. What Are The Disadvantages Of The Harmonics Present In The Inverter System? Harmonic currents will lead to excessive heating in the induction motors. This will reduce the load carrying capacity of the motor. If the control and the regulating circuits are not properly shielded, harmonics from power ride can affect their operation and malfunctioning can result. Harmonic currents cause losses in the ac system and can even some time produce resonance in the system. Under resonant conditions, the instrumentation and metering can be affected. On critical loads, torque pulsation produced by the harmonic current can be useful. 132. What Are The Methods Of Reduction Of Harmonic Content? Transformer connections Sinusoidal PWM Multiple commutation in each cycle Stepped wave inverters 133. Compare Csi And Vsi? VSI: Input voltage is maintained constant The output voltage does not depend on the load The magnitude of the output current and its waveform depends on the nature of the load impedance It requires feedback diodes Commutation circuit is complicated i.e. it contains capacitors and inductors. CSI: Input current is constant but adjustable The output current does not depend on the load The magnitude of the output voltage and its waveform depends on the nature of the load impedance It does not requires feedback diodes Commutation circuit is simple i.e. it contains only capacitors. 134. What Are The Disadvantages Of Pwm Control? SCRs are expensive as they must possess low turn-on and turn-off times. 135. What Does Ac Voltage Controller Mean? It is device which converts fixed alternating voltage into a variable voltage without change in frequency. 136. What Are The Applications Of Ac Voltage Controllers? Domestic and industrial heating Lighting control Speed control of single phase and three phase ac motors Transformer tap changing 137. What Are The Advantages Of Ac Voltage Controllers? High efficiency Flexibility in control Less maintenance 138. What Are The Disadvantages Of Ac Voltage Controllers? The main draw back is the introduction of harmonics in the supply current and the load voltage waveforms particularly at low output voltages. 139. What Are The Two Methods Of Control In Ac Voltage Controllers? ON-OFF control Phase control 140. What Is The Difference Between On-off Control And Phase Control? ON-OFF control: In this method, the thyristors are employed as switches to connect the load circuit to the source for a few cycles of the load voltage and disconnect it for another few cycles. Phase control: In this method, thyristor switches connect the load to the ac source for a portion of each half cycle of input voltage. 141. What Is The Advantage Of On-off Control? Due to zero-voltage and zero current switching of thyristors, the harmonics generated by the switching action are reduced. 142. What Is The Disadvantage Of On-off Control? This type of control is applicable in systems that have high mechanical inertia and high thermal time constant. 143. What Is The Duty Cycle In On-off Control Method? Duty cycle K = n/ (n + m), where n = number of ON cycles, m = number of OFF cycles. 144. What Is Meant By Unidirectional Or Half-wave Ac Voltage Controller? Here the power flow is controlled only during the positive half-cycle of the input voltage. 145. What Are The Disadvantages Of Unidirectional Or Half-wave Ac Voltage Controller? Due to the presence of diode on the circuit, the control range is limited and the effective RMS output voltage can be varied between 70.7% and 100%. The input current and output voltage are asymmetrical and contain a dc component.If there is an input transformer, saturation problem will occur It is only used for low power resistive load. 146. What Is Meant By Bidirectional Or Half-wave Ac Voltage Controller? Here the power flow is controlled during both cycles of the input voltage. 147. What Is The Control Range Of Firing Angle In Ac Voltage Controller With Rl Load? The control range is Φ Average output voltage, rms value of output voltage expression. 166. Describe The Working Of 3Φ Fully Controlled Bridge Converter In The Rectifying Mode And Inversion Mode. And Derive The Expressions For Average Output Voltage And Rms Output Voltage? 3Φ full converter bridge circuit waveforms of vo , io , iA, vs Operation Average output voltage expression. 167. Describe The Working Of 3Φ Semi Converter. And Derive The Expressions For Average Output Voltage And Rms Output Voltage? 3Φ semi converter bridge circuit waveforms of vo , io , iA, vs Operation Average output voltage expression. 168. Describe The Working Of Dual Converter? 3Φ dual converter bridge circuit waveforms of vo , io , vo1 , vo2 , i1, i2 , vs , ic Operation for with circulating current and without circulating current load voltage expression, peak value icp 169. For A Type A Chopper (first Quadrant), Express The Following Variables As A Function Of Vs, R And Duty Cycle In Case The Load Is Resistive Average Output Voltage And Current? chopper circuit output voltage & current waveforms Average load voltage expression 170. Describe The Principle Of Step-up Chopper. Derive An Expression For The Average Output Voltage In Terms Of Input Dc Voltage & Duty Cycle? chopper circuit output voltage & current waveforms Average load voltage expression 171. Describe The Working Of Four Quadrant Chopper? chopper circuit operation 172. Explain The Working Of Current Commutated Chopper With Aid Of Circuit Diagram And Necessary Wave Forms. Derive An Expression For Its Output Voltage? chopper circuit Modes of operation- equivalent circuit diagrams Current & voltage waveforms Design 173. Explain The Working Of Voltage Commutated Chopper With Aid Of Circuit Diagram And Necessary Waveforms. Derive An Expression For Its Output Voltage? chopper circuit Modes of operation- equivalent circuit diagrams Current & voltage waveforms Design of C & L 174. Describe The Operation Of Series Inverter With Aid Of Diagrams. Describe An Expression For Output Frequency, Current And Voltages. What Are The Disadvantages Of Basic Series Inverter? series inverter circuit Current & voltage waveforms Operation Expression for output frequency, VL, VC 175. State Different Methods Of Voltage Control Inverters. Describe About Pwm Control In Inverter? External control of ac output voltage External control of dc input voltage Internal control of Inverter PWM inverter Single pulse modulation Multiple pulse modulation Sinusoidal pulse modulation 176. Explain The Operation Of 3 Bridge Inverter For 1800 Degree Mode Of Operation With Aid Of Relevant Phase And Line Voltage Waveforms? Inverter circuit operation- equivalent circuits Waveforms of phase and line voltage 177. Explain The Operation Of 3 Bridge Inverter For 1200 Degree Mode Of Operation With Aid Of Relevant Phase And Line Voltage Waveforms? Inverter circuit Operation- equivalent circuits Waveforms of phase and line voltage 178. Draw The Circuit Diagram Of 1Φ Auto Sequential Commutated Current Source Inverter And Explain Its Operation With Equivalent Circuits For Different Modes And Necessary Waveforms? Inverter circuit Modes of operation- equivalent circuits Waveforms of ic, vc , io Expression for tc, vc, vL 179. Draw The Circuit Diagram Of 1Φ Capacitor Commutated Current Source Inverter And Explain Its Operation With Equivalent Circuits For Different Modes And Necessary Wave Forms? Inverter circuit Modes of operation- equivalent circuits Waveforms of ic, vo , io, iT1, iT2, vT1, vT2 Expression for vc, vL , vo , io, tc 180. Explain The Operation Of Multistage Control Of Ac Voltage Controllers With Neat Diagram? Circuit diagram Operation 181. Explain The Operation Of 1Φ Ac Voltage Controller With Rl Load? Circuit diagram Operation Waveforms 182. Explain The Operation Of Sequence Control Of Ac Voltage Controller? Circuit diagram Operation Waveforms 183. Explain The Operation Of 1 Sinusoidal Ac Voltage Controller? Circuit diagram Operation Waveforms 184. For A 1Φ Voltage Controller, Feeding A Resistive Load, Draw The Waveforms Of Source Voltage, Gating Signals, Output Voltage And Voltage Across The Scr. Describe The Working With Reference To Waveforms Drawn? Circuit diagram Operation Waveforms POWER ELECTRONICS Interview Questions and Answers pdf free download :: Read the full article
0 notes
Text
N1-§2 What is the Structure of a Solid-State Relay?

The solid-state relays are four-terminal active devices, two of the four terminals are input control terminals, and the other two terminals are output control terminals. Although the types and specifications of SSR switches are numerous, their structures are similar and consist mainly of three parts (as shown in Figure 2.1): Input Circuit (Control Circuit), Drive Circuit, and Output Circuit (Controlled Circuit).
Input Circuit:
The Input Circuit of the solid state relay, also called control circuit, provides a loop for the input control signal, making the control signal as a trigger source for the solid state relay. According to different input voltage types, the input circuit can be divided into three types, DC input circuit, AC input circuit and AC/DC input circuit.
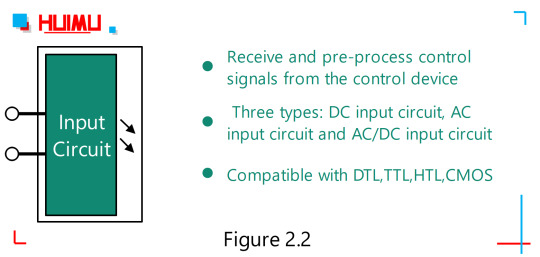
The DC input circuit can be further divided into Resistive Input Circuit and Constant Current Input Circuit. 1) The Resistive Input Circuit, whose input current increases linearly with increasing input voltage, and vice versa. If the control signal has a fixed control voltage, the resistor input circuit should be selected. 2) The Constant Current Input Circuit. When the input voltage of the constant current input circuit reaches a certain value, the current will no longer increase obviously as the voltage increases. This feature allows the use of a constant current input solid state relay over a fairly wide input voltage range. For example, when the voltage variation range of the control signal is kind of large (e.g., 3~32V), the DC solid state relay with constant current input circuit will be recommended to ensure that the DC solid-state relay can work reliably over the entire input voltage range. Some of these input control circuits have positive and negative logic control, inverting and other functions, as well as the compatibility of logic circuits. Thus, solid state relays can be easily connected to TTL circuits (Transistor-Transistor Logic circuits), CMOS circuits (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor circuits), DTL circuits (Diode-Transistor Logic circuits), and HTL circuits (High Threshold Logic circuits). At present, DTL has been gradually replaced by TTL, and HTL has been replaced by CMOS. And if the Pulse Width Modulated signal (PWM) is used as input signal, the ON/OFF switching frequency of the AC load supply should be set to less than 10Hz, or the output switching rate of the output circuit of the AC SSR cannot keep up with it.
Drive Circuit:
The driving circuit of solid state relay includes three parts: Isolation Coupling Circuit, Function Circuit and Trigger Circuit. However, according to the actual needs of solid-state relay, only one/two of these parts may be included.

1. Isolated Coupling Circuit:
The isolation and coupling methods for I/O circuits (Input / Output circuit) of solid-state relays currently use two ways, Optocoupler Circuits and High Frequency Transformer Circuits. 1) Optocoupler (also called photocoupler, optical coupler, opto-isolator, or optical isolator) is opaquely packaged with an infrared LED (Light-Emitting Diode) and an optical sensor to achieve isolated control between "control side" and "load side", because there is no electrical connection or physical connection between the " Light emitter " and the " Light sensor" except the beam. The types of “source-sensor” combinations normally include: "LED-Phototransistor" (Phototransistor Coupler), "LED-Triac" (Phototriac Coupler), and "LED-Photodiode array" (the stack of photodiodes is used to drive a pair of MOSFETs or an IGBT). 2) The high frequency transformer coupling circuit uses a high frequency transformer to convert the control signal at the input to the drive signal at the output. The detail process is, the input control signal produces a self-oscillating high frequency signal that will be transmitted through the transformer core to the transformer secondary, and after processing by the detection/rectification circuit and the logic circuit, the signal will eventually become the drive signal to drive the trigger circuit.
2. Functional Circuit:
The functional circuit may include various functional circuits, such as detection circuit, rectifier circuit, zero-crossing circuit, acceleration circuit, protection circuit, display circuit, etc.
3. Trigger Circuit:
The trigger circuit is used to provide a trigger signal to the output circuit.
Output Circuit:
The output circuit of the solid-state relay is controlled by a trigger signal to enable on/off switching of the load power supplies.
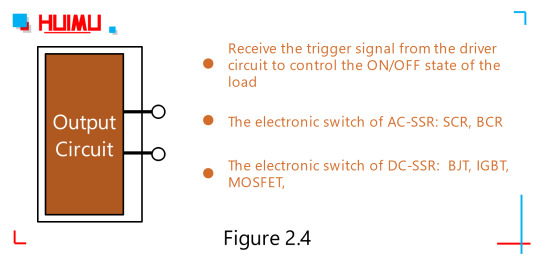
The output circuit is mainly composed of an output component (chip) and an absorption loop (which acts as a transient suppressor), and sometimes includes a feedback circuit. Up to now, the output component of solid state relays mainly include:Bipolar Junction Transistor(Bipolar Transistor or BJT, which divided of two types, PNP and NPN), Thyristor (Silicon Controlled Rectifier or SCR), Triac (Bi-directional Triode, Bi-directional thyristor, Bi-directional Controlled Rectifier or BCR), Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET), Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor(IGBT), Silicon-Carbide MOSFET (SIC MOSFET, a kind of wide bandgap transistor with the industrial grade highest operating junction temperature of 200°C, low power consumption and compact size), and so on. The output circuit of the solid state relay can be divided into three types: DC output circuit, AC output circuit and AC/DC output circuit. The DC output circuit typically uses bipolar component (such as IGBT or MOSFET) as the output component, and the AC output circuit usually uses two Thyristors or one Triac as the output component.
0 notes
Text
Global Optocouplers Market 2019 - Evolving Technology, Trends, Key Market segments and Industry Analysis

An optocouplers, also called opto-isolator, optical coupler, opto coupler, photocoupler or optocouplers, is a passive optical component that can combine or split transmission data (optical power) from optical fibers. It is an electronic device which is designed to transfer electrical signals by using light waves in order to provide coupling with electrical isolation between its input and output. The main purpose of an optocoupler is to prevent rapidly changing voltages or high voltages on one side of a circuit from distorting transmissions or damaging components on the other side of the circuit.
An optocoupler contains a light source often near an LED which converts electrical input signal into light, a closed optical channel and a photosensor, which detects incoming light and either modulates electric current flowing from an external power supply or generates electric energy directly. The sensor can either be a photoresistor, a silicon-controlled rectifier, a photodiode, a phototransistor or a triac.
Request Sample Report@ https://www.acquiremarketresearch.com/sample-request/478
The market is driven by various end-user industries, such as Telecommunications, Cable TV, Military and Aerospace, Industrial Motors, Automotive and others (computers and office equipment, plasma displays).
The market for Optocouplers is fragmented with players such as Fairchild, Toshiba, Avago (FIT), Vishay Intertechnology, Renesas, Sharp, ISOCOM, LiteOn, Everlight Electronics, Standex-Meder, Electronics, IXYS Corporation, Kingbright Electronic, NTE Electronics, Plus Opto, etc. The industry is expected to remain innovation-led, with frequent acquisitions and strategic alliances adopted as the key strategies by the players to increase their industry presence. Meanwhile, optimize product mix and further develop value-added capabilities to maximize margins.
The unique characteristics of Optocouplers, together with their growing significance in multi-channel and bi-directional applications, are anticipated to boost sales. Manufacturers can take advantage of this situation by reinforcing their production units and supply-chains to avoid any delay in production turn-around-times (TAT) and supply-lead-times.
According to this study, over the next five years the Optocouplers market will register a 8.3% CAGR in terms of revenue, the global market size will reach US$ 4780 million by 2024, from US$ 2970 million in 2019. In particular, this report presents the global market share (sales and revenue) of key companies in Optocouplers business.
This report presents a comprehensive overview, market shares, and growth opportunities of Optocouplers market by product type, application, key manufacturers and key regions and countries.
More Info and TOC @ https://www.acquiremarketresearch.com/industry-reports/global-optocouplers-market-growth-2019-2024/478/
This study considers the Optocouplers value and volume generated from the sales of the following segments:
Segmentation by product type
Non-linear Optocouplers
Linear Optocouplers
Segmentation by application
Telecommunications
Cable TV
Military and Aerospace
Industrial Motors
Automotive
Others
This report also splits the market by region
Americas
APAC
Europe
Middle East & Africa
The report also presents the market competition landscape and a corresponding detailed analysis of the major vendor/manufacturers in the market.
The key manufacturers covered in this report
Fairchild, Toshiba, Avago (FIT), Vishay Intertechnology, Renesas, Sharp, ISOCOM, LiteOn, Everlight Electronics, Standex-Meder Electronics, IXYS Corporation, Kingbright Electronic, NTE Electronics, Plus Opto….
In addition, this report discusses the key drivers influencing market growth, opportunities, the challenges and the risks faced by key manufacturers and the market as a whole. It also analyzes key emerging trends and their impact on present and future development.
Research objectives
To study and analyze the global Optocouplers consumption (value & volume) by key regions/countries, product type and application, history data from 2014 to 2018, and forecast to 2024.
To understand the structure of Optocouplers market by identifying its various subsegments.
Focuses on the key global Optocouplers manufacturers, to define, describe and analyze the sales volume, value, market share, market competition landscape, SWOT analysis and development plans in next few years.
To analyze the Optocouplers with respect to individual growth trends, future prospects, and their contribution to the total market.
To share detailed information about the key factors influencing the growth of the market (growth potential, opportunities, drivers, industry-specific challenges and risks).
To project the consumption of Optocouplers submarkets, with respect to key regions (along with their respective key countries).
To analyze competitive developments such as expansions, agreements, new product launches, and acquisitions in the market.
To strategically profile the key players and comprehensively analyze their growth strategies.
Request for Discount @ https://www.acquiremarketresearch.com/discount-request/478
About Acquire Market Research:
Acquire Market Research is a shrine of world-class research reports from around the world and we offer you only the best in the Industry when it comes to research. At Acquire, every data need will be catered to and met with a powerful world of choices. "We understand the integral role data plays in the growth of Business empires."
Contact Us: 555 Madison Avenue, 5th Floor, Manhattan, New York, 10022 USA Phone No.: +1 (800) 663-5579 Email ID:[email protected]
0 notes